It’s important in a Singapore style program for students to understand bar model drawing as a tool to help visualize relationships between the known and unknown in a word problem. It helps students see the algebraic structure in problems in a more concrete manner. Developed by a Primary Mathematics Project team of the Curriculum Development Institute of Singapore in the 1980’s, the Model Method for problem solving (as it’s known in Singapore) was designed as a pictorial stage to help students learn abstract mathematics.
The model method has been incorporated into the Progressions documents for the Common Core State Standards for Math (CCSSM) as a “tape diagram”. The CCSSM glossary defines a tape diagram as:
“A drawing that looks like a segment of tape, used to illustrate number relationships. Also known as a strip diagram, bar model, fraction strip, or length model.”
As such, bar models are becoming ubiquitous in elementary schools. Books have been written about Singapore’s model method, my favorite being The Singapore Model Method for Learning Mathematics:
There’s plenty to be covered with bar models, and I thought I’d share answers to the most commonly asked questions I get from teachers on model drawing:
How do you get kids to draw models when they already know the math?
How do you assess them?
When models are introduced in Singapore textbooks, the problems are very simple and students will typically know what operation to use. The first part whole models in Primary Mathematics, Common Core Edition are in the 3A textbook:

And the first part-whole model lessons in Math in Focus are in 2A:
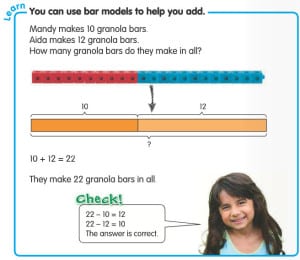
Those are pretty easy word problems and most kids are waving their hands, with that “I KNOW the answer” look on their faces. It’s important to reiterate to students, “I’m sure you know the answer and even the equation to get there. What we’re learning today is a new way of drawing a model for our word problem so that we can work with more challenging problems in third grade. Problems like”:
A father shares $60 among his three sons and one daughter. If the daughter gets twice the amount that each son gets, how much money does his daughter receive?
We’ll come back to that one.
When assessing word problems, the solution method is a significant part of the answer. Students should expect to show their work to get full credit for a problem. As a teacher, it’s important to keep in mind that there is no one-way to draw a bar model.
A word problem might consist of points for the method of solving as well as points for correct computation and answers. To encourage students to draw and become proficient with bar models, I have used a rubric for assessment:
- 1 point for a representative diagram – Does the model make mathematical sense?
- 1 point for correct labeling, including the “?” to represent what is unknown.
- 1 point for computation on the first step and, if more than one step…
- 1 point for computation on the second or more steps
- 1 point for a correct answer in a complete sentence
Let’s look at an example. This is a student-written two-step word problem from third grade:
Does the bar model make sense? +1 point
Are the bars labeled? Are question marks in the correct places? +1 point
Is the computation to figure out the value of one unit correct? 384 ÷ 6 = 64 +1 point
How about the computation on the second step? 64 x 5 = 320 +1 point
Is the answer in a complete sentence? +1 point
So, what’s the deal with the 64 ÷ 6 equation? A byproduct of requiring students to show their work is that oftentimes, they will leave work on the paper, just in case. As a teacher, I love that this provides me with some insight into this student’s thought process:
I’m pretty sure I know what I’m doing, but I still am a little confused.
Which is exactly what the student said when I asked her about the extra equation. She realized her answer couldn’t be right because:
I ended up with 14 remainder 4 meatballs, and how could that happen?
Without a system to evaluate, you end up with:
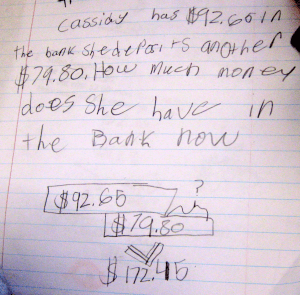
I’m drawing boxes because I’m supposed to… I don’t get it.
This model doesn’t make sense. The student’s computation is slightly off, but she knows she needs to add. A teacher can also see from this model that more re-teaching and practice is necessary for this student and probably others in the class.
As students progress, the rubric may change. At the end of a unit/school year, the same problem might be worth three points; one apiece for diagram, computation, solution. I often tell students, “You don’t need to draw the model if you feel you understand the problem, however, you will be graded either all correct or all incorrect. Without the models I can’t give you partial credit for your thinking.”
Most students draw them anyway as a way to check their work. Some just start to see them in their heads. Here are a couple of examples from the end of a fractions unit in 5A
How would drawing a model have helped this student?

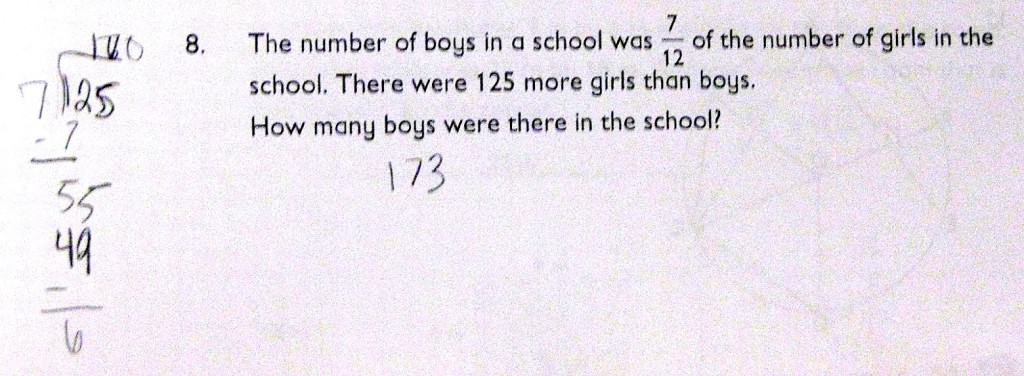

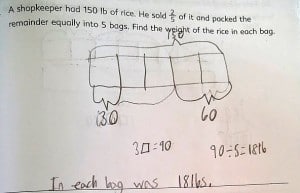




















Thanks for your explanation. in what grade should model drawing begin? We are using Singapore Standards Edition and there’s nothing in the first grade book about the model drawing that you’re showing above.
Good question. Model drawing is first introduced in Primary Mathematics 3A books. Math in Focus and Many Pals are Here series have the first lessons in 2A materials. Supplemental books will have bar models earlier. If you’re looking to introduce bar models to younger students, the Thinking Blocks website offers an online version of their tool with numbers to 20.
Thanks so much!
I just love you Cassy. I have one child who has graduated and another in high school (who has been told not to bar model) but that is another story. If you remember I taught Singapore math at a charter school here in Utah for three years. It just makes my heart smile to see you out there spreading the word and showing people how easy it makes math. I have former students doing very well in math in high school and they thank me. Keep spreading the word. We need you here in the US. Maybe eventually people will get how fun and simple math can be, not hate it like the majority of kids and we could end up in the top ten in TIMMS. You are amazing. Keep up the wonderful work and thank you, thank you, thank you.
Cindy Dale
Aw Cindy, you’re making me blush. Thanks for your kind words!